“Bytes: Practical Research for CSR” is a series by Give Grants designed to decode and demystify the extensive social impact research and data available in the form of clear and actionable insights for CSR practitioners in India.”
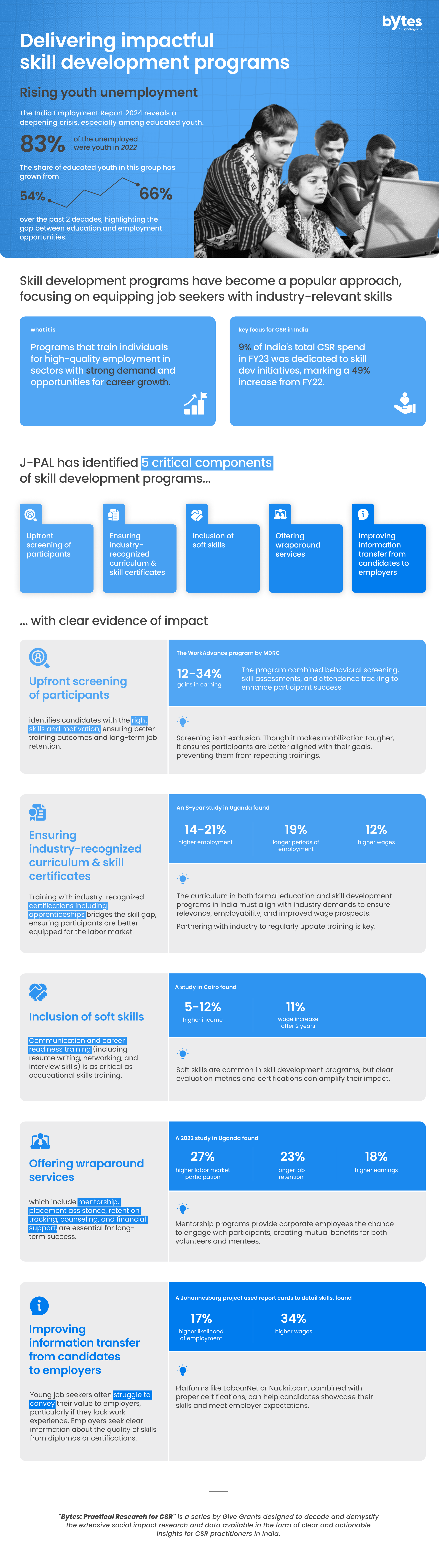
The India Employment Report 2024 highlights the growing unemployment crisis among India’s youth, particularly those with secondary or higher education.
- In 2022, 83% of the unemployed population were young people.
- The share of educated youth among the unemployed rose from 54% to 66% over the past 2 decades.
Over the years, multiple solutions have emerged to address unemployment, with skill development programs being a popular approach, though their success varies. These programs focus on training job seekers for high-quality employment in industries with strong labor demand and career growth opportunities.
Skill development is a key focus in many CSR portfolios, both in India as well as globally, as standalone initiatives or integrated into larger programs.
- In FY23, 9% of India’s total CSR spending was dedicated to skill development initiatives, marking a 49% increase compared to FY22.
- 201 top CSR spenders contributed INR 2,010 crore to 913 skill development projects in FY23.
J-PAL has defined 5 critical components of skill development programs based on evaluation outcomes in more than six countries





A) Upfront screening of participants
Upfront screening for applicants on basic skills and motivation ensures higher training completion rates and longer retention at first employment.
- The WorkAdvance program by MDRC, implemented in three U.S. counties, uses a thorough screening process to guide participants toward quality jobs in sectors with growth opportunities. Subtle methods like behavioral screening, skill assessments, and monitoring attendance ensure better alignment between participants’ aspirations and program offerings. This approach has resulted in 12-34% earnings gains after training.(ref) While the gain may not solely be due to screening, poor screening can cause a mismatch between participants’ aspirations and program offerings, leading to higher dropout rates.
Screening isn’t exclusion. Though it makes mobilization tougher, it ensures participants are better aligned with their goals, preventing them from repeating training.
B) Ensuring industry-recognized curriculum & skill certificates
- An eight-year study in Uganda assessed the impact of sector-focused vocational training and on-the-job practicals, revealing a 14-21% higher likelihood of employment, 19% longer employment periods, and 12% higher hourly wages.(ref)
C) Including soft skills
Communication and career-readiness training is as critical as occupational skills training. It should include an introduction to resume templates, professional networking platforms, and representation skills for interviews.
- A study conducted in Cairo, Egypt found that the soft skills component added an incremental 5-12% higher income on the first job taken up by the participants.(ref)
- However, soft skills must be supported by industry-recognized certifications, with research showing 11% higher earnings for workers two years after receiving such certifications.(ref)
Soft skills are part of most CSR-supported skilling programs, but defining evaluation metrics and certifications would improve impact. Some of the most widely recognized soft skills certifications in India are offered in partnership with IIT Mumbai, IIT Kanpur, and Delhi University.
D) Offering wraparound services
In addition to the industry-aligned skills and soft skills certifications, components like mentorships, placement assistance, retention tracking, counseling to handle workplace dynamics, and financial support become critical. These components are referred to as wraparound services.
- A 2022 J-PAL study in Uganda found that students who received mentorship and a small unconditional cash transfer at program completion had 27% higher labor market participation, stayed in their first job 23% longer, and earned 18% more than non-mentored students.
The mentorship program offers corporate employees from funding CSR companies a valuable opportunity to build closer relationships with program participants. It holds immense potential to benefit both the participants and the volunteers.
E) Improving the information transfer from the candidates to the employers
Young job seekers often struggle to convey their potential value to employers, especially if they lack prior work experience.(ref) Employers value information about the quality of skills reflected in diplomas or training certificates.
- A project in Johannesburg, South Africa, introduced report cards detailing candidates’ skill levels (similar to TOEFL scores), resulting in a 17% higher likelihood of employment and 34% higher weekly wages.
Independent platforms like LabourNet or established networks like Naukri.com, when properly structured and paired with the right certifications, can bridge this gap and help participants provide employers with the necessary information to make informed hiring decisions.
[Infographic] Delivering impactful skill development programs